"Tomcat" is a small insect that looks almost like a long ant, usually with a black-brown body. Tomcat leaves burn-like spots on human skin. With each passing day, the pain and itching intensify, forming blisters (similar to herpes).
What kind of bugs are these?

The scientific name of this insect is Paederus littorarius, Paederus fuscipes. It is approximately 7-10 millimeters in length.
This beetle is actually classified as a beneficial insect because it acts as an active predator of certain pests of rice plants, such as brown leafhoppers, white-backed planthoppers, zigzag leafhoppers, green leafhoppers, and soybean pests.
Tomcats often appear at dusk. At night, they are attracted to incandescent and neon lights, accidentally coming into contact with human habitats.
The active spread of tomcats usually occurs during the rainy season or after the rainy season. An increase in the number of these roaming beetles indicates a change in the environmental balance due to changes in land use or changes in extreme weather conditions, such as a prolonged rainy season.
Danger
This beetle does not bite or sting. Toxins are released when the beetle is crushed or accidentally squeezed. Direct or indirect exposure (spreading insect toxin manually or through towels, clothing, or other equipment contaminated with insect poison) can cause skin or eye irritation.
The beetle's blood (hemolymph) contains a dangerous animal poison called pederin (C24H43O9N), which is 12 times more toxic than cobra venom.
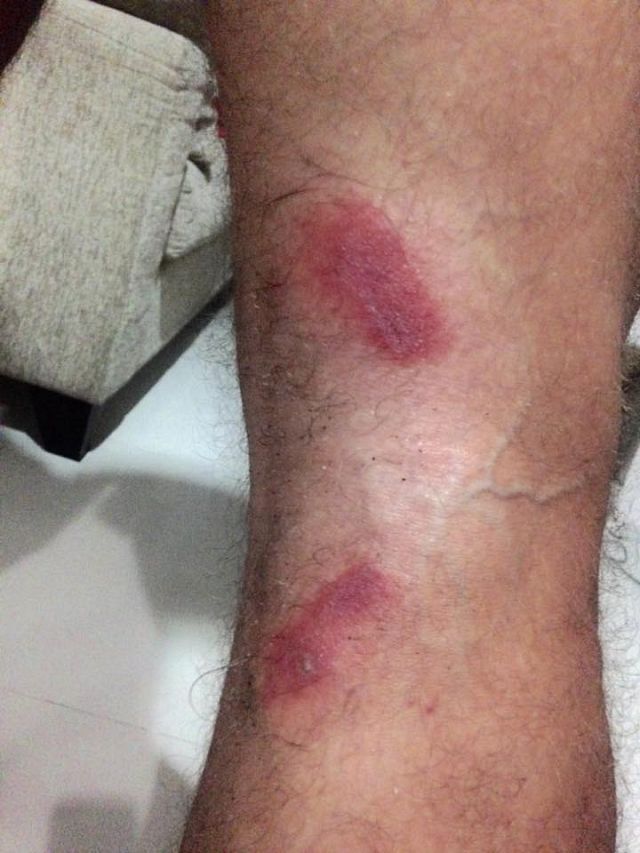
In its dry form, this poison remains toxic for up to 8 years. The inflammatory skin reaction due to the impact of these toxins activates inflammatory mediators. The release of cytokines causes a burning sensation in the affected area of the skin, followed by erythematous plaques with blisters appearing within 12-36 hours. The lesions dry up to scabs within a week.
Symptoms of Paederus toxin exposure
Forms of dermatitis manifested as linear dermatitis or whip dermatitis.
Superficial lesions do not cause scars, but if the skin is affected, it will appear ulcerated. Sometimes the disease is difficult to distinguish from herpes zoster or herpes zoster, and the difference lies in the nature of the spread.
Acute vesicular lesions completely heal within 10-12 days with temporary post-inflammatory black spots.
Symptoms of Paederus dermatitis can be mild, moderate, and may be accompanied by secondary infection in the affected area.
Mild symptoms include mild intense redness of the skin (erythema), which begins after 24 hours and lasts about 48 hours. The patient complains of burning, burning, and itching. Approximately 48 hours later, the vesicular (blister) stage follows, with a gradual increase in blisters and reaching a maximum within 48 hours.
The blisters dry out in about 8 days, peeling off to leave a thin linear hyperpigmentation with wrinkles on the affected area of the skin, which can persist for a month or more.
Severe symptoms include abrasions and pigment scars, usually more extensive. Toxins can cause neuralgia, arthralgia, fever, and vomiting. Intense redness of the skin can last for several months.
How to treat
Damage caused by tomcat is an irritating contact dermatitis. Therefore, a reasonable approach is to wash the affected area with clean water and soap. This can prevent the development of linear dermatitis or its more severe forms.
To relieve irritation, use corticosteroid ointments such as hydrocortisone (HYDROCORTISONE, THECORT). Take antihistamines like Claritin (CLARITIN), cetirizine (INTRIZIN).
The use of antibacterial ointment - gentamicin (GENTAMICYN, GARAMYCIN) or oral antibiotics may be possible because areas exposed to pederin toxin may become contaminated.
How to protect yourself from tomcat
If you notice at least one tomcat, be sure to thoroughly shake all clothes, bedding, and do wet cleaning in your home and yard. Buy an insect repellent canister and spray it outside the house around the perimeter.
If the beetle lands on you, try to gently shake it off. Wash all areas of the skin that have come into contact with the beetle.
Turn off fluorescent lights at night or switch to incandescent bulbs.
Keep doors and windows closed. Sleep with a mosquito net.
Check the bed and walls near the bed for beetles before going to bed.
You can add one right now!